Azure Container Hosting
The Azure Container Host is an alternate execution mode for the cloud custodian azure provider. Running the Azure Container Host is done with the official custodian docker image. See the ACI and Kubernetes deployment tutorials to get started running the Azure Container Host.
Overview
The Azure Container Host will periodically scan azure blob storage for a set of custodian policies to execute in either a periodic or event based mode against a target subscription. For periodic policies, the container host will execute the policy on the cron schedule that is provided. For event based policies, the container host maintains an azure queue that subscribes to events in the target azure subscription.
Once the Azure Container Host is deployed, any policies uploaded to blob storage are automatically loaded and running against an Azure Subscription. This makes it very easy to manage and run a large number of policies.
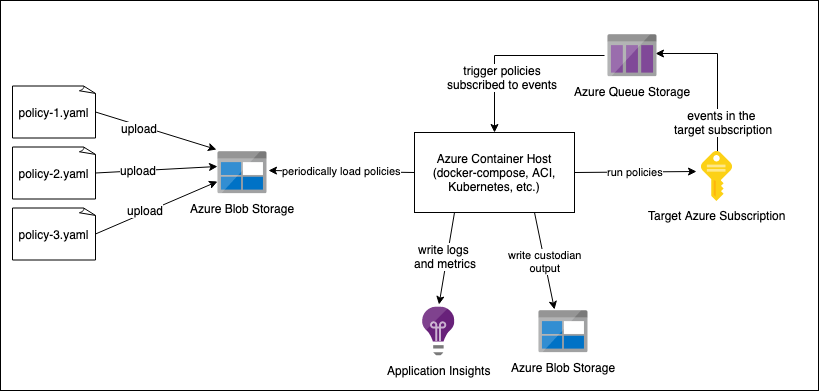
It is also possible to configure a set of container hosts to each monitor an Azure Subscription. This can be useful for monitoring a Management Group or other collections of subscriptions. These Container Hosts could be managed with any container orchestration, but we provide the tooling and a tutorial for deploying container hosts inside Kubernetes with a Helm chart.
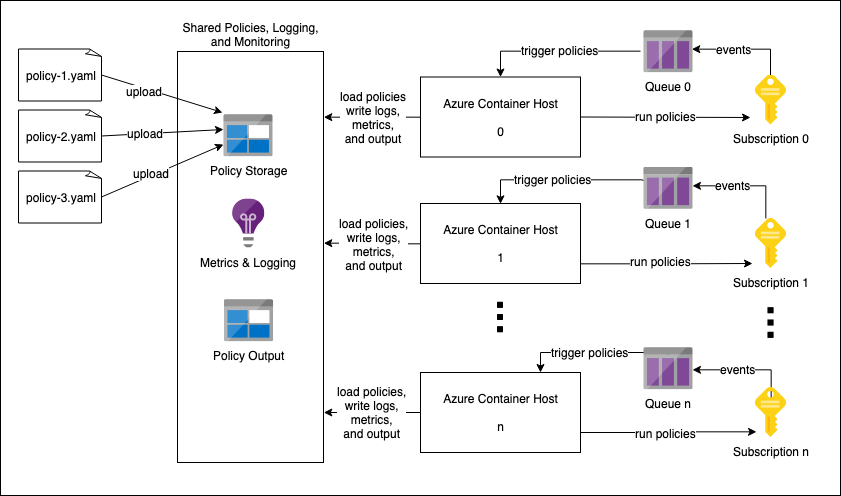
In this diagram, each Container Host is reading and writing to the same policy and monitoring resources, but they could each be configured to interact with their own Storage Accounts or Application Insights instances.
Supported Policy Modes
The container host will only run policies with one of the following modes specified. Otherwise, the policy will be ignored.
Periodic
Periodic policies must specify a mode with type container-periodic and a cron schedule. This
schedule can specify when the policy should run. For example: once every hour, on midnight on every
weekday, or once a month.
policies:
- name: run-every-day-at-midnight
resource: azure.resourcegroup
mode:
type: container-periodic
schedule: '0 0 * * *'
properties:
execution-options:
type: object
schedule:
pattern: ^\s?(\*|[0-9]|\,|\/|\-)+ (\*|[0-9]|\,|\/|\-)+ (\*|[1-9]|[1-2][0-9]|3[0-1]|\,|\*\/|\-)+
(jan|feb|mar|apr|may|jun|jul|aug|sep|oct|nov|dec|\,|\*\/|[1-9]|1[0-2]|\*)+ (mon|tue|wed|thu|fri|sat|sun|[0-6]|\,|\*|\-)+\s?$
type: string
type:
enum:
- container-periodic
required:
- type
Event Based
Event based policies must specify a mode with the type container-event and a set of events that
will trigger the execution. For example: after a new resource group is created.
policies:
- name: run-on-new-resource-group
resource: azure.resourcegroup
mode:
type: container-event
events:
- resourceProvider: Microsoft.Resources/subscriptions/resourceGroups
event: write
properties:
events:
items:
oneOf:
- type: string
- properties:
event:
type: string
resourceProvider:
type: string
required:
- resourceProvider
- event
type: object
type: array
execution-options:
type: object
type:
enum:
- container-event
required:
- type
Configuration
Configuration for the container host is provided as environment variables. There are several environment variables specific to the container host:
Variable Name |
Required |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
required |
The URL to the azure blob container to load custodian policies from. |
|
required |
The resource id of the storage account to hold the event queue. |
|
The name of the event queue that the container host will listen on. If this does not exist, it will be created. Defaults to the target subscripition id. |
|
|
The application insights to send log output to. In the format: |
|
|
The application insights to send metrics output to. In the format: |
|
|
The URL of the storage account blob container to send log output to. In the format: |
In addition to the above environment variables, authentication must be provided to the container host. See Authentication & Access for authenticating the container host with an azure identity.
Once an identity has been established, it will need the following roles in azure:
ReaderandStorage Blob Data Contributoron the Storage Account that holds the policy files.ContributorandStorage Queue Message Processoron the Storage Account that the event queue will live in.Any other roles that are needed to run the policies that the container host will run. For example, if there is a policy that filters the
azure.vmresource, theReaderrole will be required for the VMs that are in the container host’s target subscription.
Running Locally
The container host can be run locally with python -m c7n_azure.container_host.host.
You will need to provide all of the same configuration specified above through either environment
variables or CLI options. Run python -m c7n_azure.container_host.host --help for more information.
Deployment Options
For quick deployments, we provide tooling for 2 methods of deploying the Azure Container Host: ACI, and Kubernetes with a Helm chart.